Passive Investing in Fast Food Chains: A Comprehensive Guide
The allure of fast food is undeniable. From the comforting familiarity of a burger and fries to the quick and convenient nature of a drive-thru, these establishments have become ingrained in our culture. This widespread appeal, coupled with the industry’s resilience, makes fast food chains an attractive prospect for investors. While actively running a franchise requires significant capital and effort, passive investing offers a way to participate in the industry’s growth without the day-to-day operational responsibilities. This comprehensive guide will explore various avenues for passive investment in fast food chains, outlining the potential benefits, risks, and key considerations.
Understanding Passive Investing
Passive investing, in its essence, involves allocating capital to investments with minimal active management. The goal is to generate returns over time without requiring constant monitoring or decision-making. This approach contrasts with active investing, where investors frequently buy and sell assets based on market fluctuations and perceived opportunities. Passive investing is often associated with long-term strategies, focusing on consistent growth and compounding returns.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Food-industry-etf_final-b830a8bad5084bd29db3806e97121474.png)
Why Consider Passive Investment in Fast Food?
Several factors contribute to the appeal of passive investing in the fast food sector:
Established Industry: Fast food is a mature and well-established industry with a proven track record. This stability can provide a degree of predictability for investors.
Avenues for Passive Investment in Fast Food
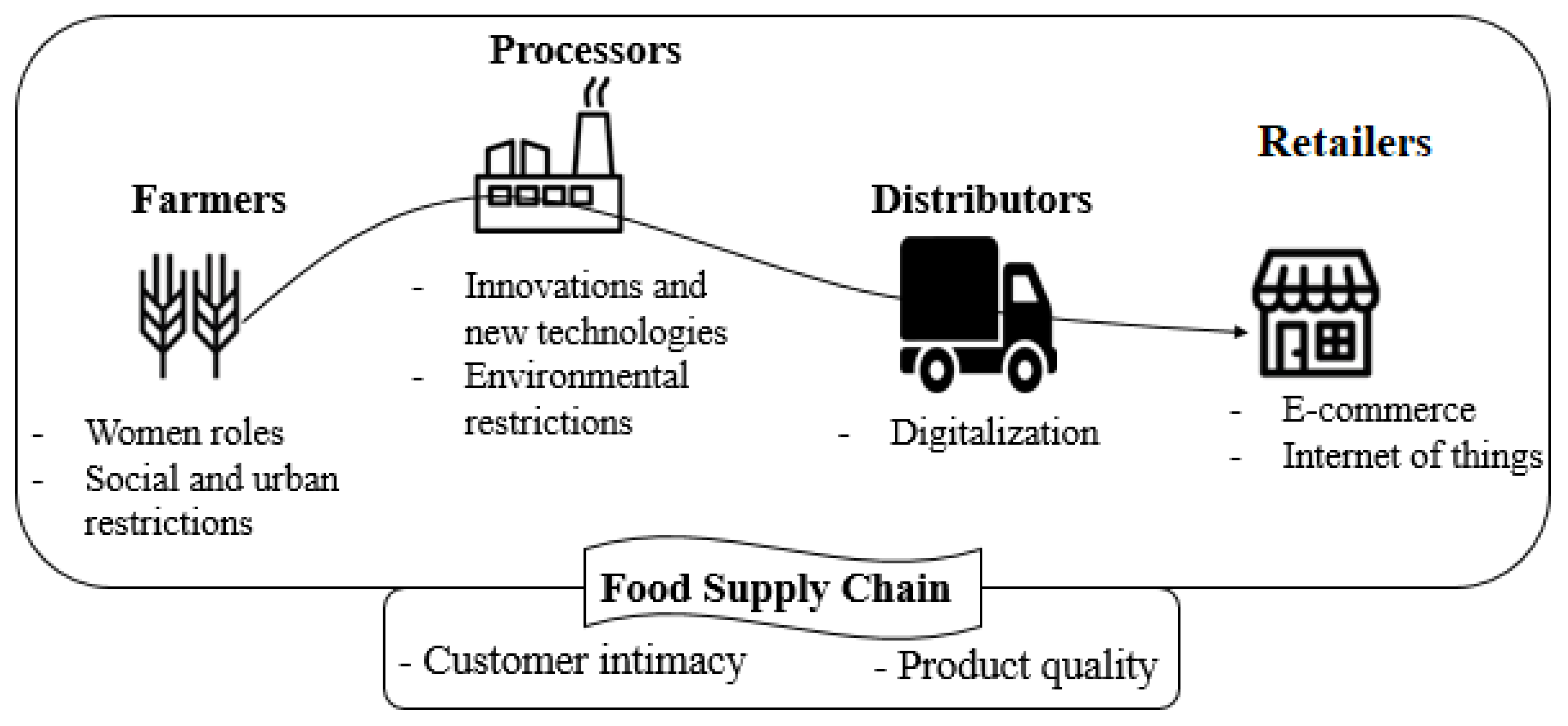
Several avenues exist for passive investors to gain exposure to the fast food industry:
# 1. Investing in Publicly Traded Fast Food Companies
Stocks: Purchasing shares of publicly traded fast food companies is the most direct form of passive investment. Investors can buy individual stocks or invest in index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the performance of the restaurant sector.
# 2. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
# 3. Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private Equity Funds: Some private equity firms invest in fast food chains, either directly or through leveraged buyouts. Investing in these funds can provide access to the fast food industry, but it typically requires a higher minimum investment and a longer investment horizon.
# 4. Franchising (Limited Passive Involvement)
Evaluating Fast Food Investment Opportunities
Before investing in any fast food venture, conducting thorough research and due diligence is crucial. Consider the following factors:
# 1. Financial Performance
Revenue and Profit Growth: Analyze the company’s historical financial performance, including revenue growth, profitability margins, and return on investment.
# 2. Brand Strength and Market Position
Brand Recognition and Reputation: Evaluate the company’s brand recognition, customer loyalty, and overall reputation.
# 3. Management Team
Experience and Track Record: Evaluate the experience and track record of the company’s management team.
# 4. Industry Trends
Consumer Preferences: Stay informed about evolving consumer preferences, including trends towards healthier options, sustainable practices, and digital ordering.
Risks Associated with Fast Food Investment
While passive investing in fast food can offer attractive returns, it’s essential to acknowledge the associated risks:
# 1. Economic Downturns
# 2. Changing Consumer Preferences
# 3. Competition
# 4. Regulatory Changes
Minimum Wage Increases: Increases in minimum wage can impact labor costs for fast food chains, potentially affecting profitability.
# 5. Brand Reputation
Diversification and Long-Term Perspective
Diversification is a cornerstone of successful passive investing. Avoid concentrating your investments in a single fast food company or investment vehicle. Spread your capital across different companies, sectors, and asset classes to mitigate risk. Adopting a long-term perspective is also crucial. Passive investing is not about quick profits; it’s about building wealth over time through consistent growth and compounding returns.
Conclusion
Passive investing in fast food chains offers a compelling opportunity to participate in a stable and established industry with potential for long-term growth. However, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research, understand the associated risks, and diversify your investments. By carefully considering the various avenues available and adopting a disciplined approach, passive investors can potentially reap the rewards of this dynamic sector. Remember that this information is for educational purposes and does not constitute financial advice. Consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Food-industry-etf_final-b830a8bad5084bd29db3806e97121474.png?w=1920&resize=1920,1267&ssl=1)